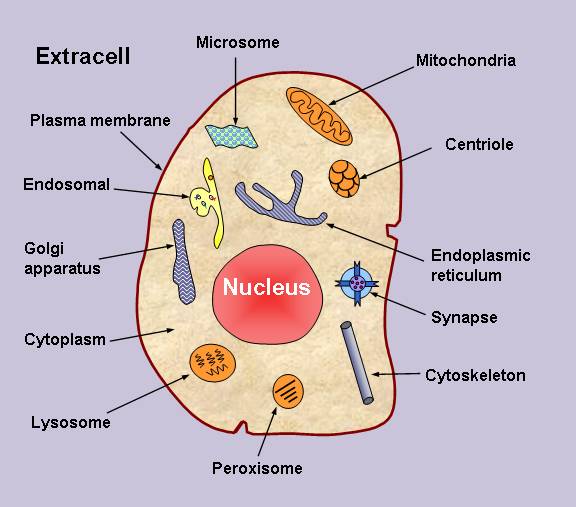
Application scope: The predictor is for human protein
samples that covers the following 14 subcellular locations:
(1) centriole, (2) cytoplasm, (3) cytoskeleton, (4) endoplasmic reticulum, (5) endosome , (6) extracell, (7) Golgi apparatus, (8) lysosome, (9) microsome, (10) mitochondrion, (11) nucleus, (12) peroxisome, (13) plasma membrane, and (14) synapse (See the Figure below).
Stop prediction if the query protein is known not a human protein or not one of the above 14 locations, because the result obtained will not make any sense.
|