
| Predicting pupylation sites in prokaryotic proteins
using pseudo amino acid composition and extreme learning machine
Introduction Prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein (Pup) can attach to specific lysine (K) residues of substrate proteins by forming isopeptide bonds for the selective degradation of proteins in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). Pupylation, one of the most important post-translational modifications of prokaryotic proteins, plays a key role in regulating a wild range of biological processes. In order to comprehensively understand these pupylation-related biological processes, identification of pupylated proteins along with pupylation sites is the first step. The traditional wet-lab experimental approaches are laborious and time-consuming to identify pupylations sites. To timely and effectively discover pupylation sites, here a novel computational predictor is proposed constructed on the Pseudo amino acid composition (PseAAC) encoding with extreme learning machine (ELM). The jackknife cross-validation on the training set show that the AUC value reached 0.6483, and an AUC of 0.6779 was obtained on the independent set. Our results also demonstrate that we can achieve performances that are very comparable or better than the state-of-the art methods with much faster speed, which is promising for analyzing large-scale biological data. PupS software MATLAB code Figure 1 shows the Diagram of pupylation sites prediction and click here to download the whole software MATLAB code.  Figure 1. The flowchart which demonstrates how our method works. Sequence analysis Figure 2 shows sequence analysis of the position-specific and non position-specific attributes, the non-redandunt dataset (including 135 traning set and 10 independent testing set) is availabe by clicking here. 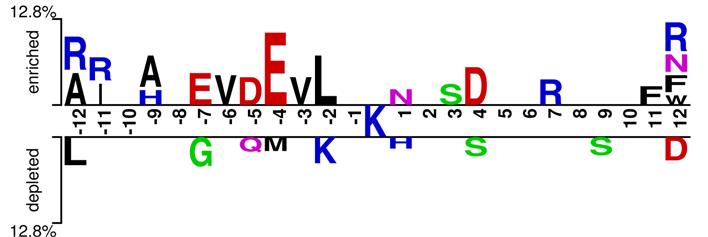 Figure 2. The two sample logo of the position-specific residue composition in the vicinity of the 174 pupypation sites and 2207 non-pupylation sites with w=25. Only amino acid residues significantly enriched and depleted (P<0.05; t-test) are shown. Reference Yong-Xian Fan, Hong-Bin Shen, Predicting pupylation sites in prokaryotic proteins using pseudo amino acid composition and extreme learning machine, 2014, 128: 267-272. |